November 24, 2017, 12:00 pm EST
 As we head into the Thanksgiving day weekend, let’s talk about oil and Saudi Arabia.
As we head into the Thanksgiving day weekend, let’s talk about oil and Saudi Arabia.
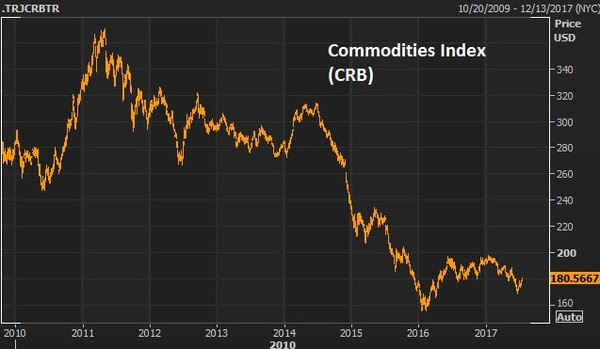
On Thanksgiving night three years ago oil was trading around $73, when the Saudis blocked a vote on an OPEC production cut. Oil dropped 10% that night, and that set off a massive oil price bust that ultimately bottomed out early last year at $26.
The goal of the Saudis was to put the emerging, competitive U.S. shale industry out of business–to force oil prices lower so that these shale companies couldn’t product profitably. The plan: They go away, and Saudi Arabia retains its power on global oil. It nearly worked. Shale companies started dropping like flies, with more than 100 bankruptcies between 2015 and 2016.
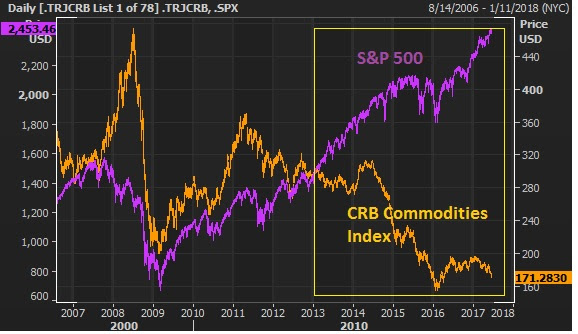
But cheap oil had broader implications for the global economy, following the Great Recession. It exposed the global banks that had lent the shale industry hundreds of billions of dollars.
Additionally, collapsing oil prices directly weighed on inflation measures and the inflation expectations. That was bad news for the central banks that had committed trillions of dollars to avert a deflationary spiral and promote a normalization of inflation. High inflation is bad. Deflation is worse. Once a deflationary mindset takes hold, it feeds into more deflation. Central banks can raise rates to kill inflation. They have few tools to fight deflation (especially after the financial crisis).
So cheap oil became bad news for the fragile global economic recovery. With that, central banks stepped in early last year and responded with coordinated easing (which included direct asset purchases, which likely included outright oil and oil-related ETFs). Oil bottomed the day the Bank of Japan intervened in the currency market, and prices jumped 50% in a month as other major central banks followed with intervention.
Now, the other piece of this story: cheap oil damaged the shale industry and the global economy, but it also damaged the same folks that set the collapse into motion–Saudi Arabia and other oil producing countries. These countries, which are heavily reliant on oil revenues, have seen their budget deficits balloon. So, with all of the above in mind, in November of last year, the oil producing countries (led by Saudi Arabia) reversed course on their plan, by promising the first production cuts since 2008.
Oil prices have now recovered to the mid-$50s. And since OPEC announced production cuts last year at this time, U.S. petroleum supply has drawn down 5%. Meanwhile, global demand is running far hotter than forecasts of last year. Yet, OPEC is extending their production cuts into this market and may get even bolder next week at their November meeting. Why? Because now it suits them. Remember, Saudi Arabia’s next king has been cleaning house over the past two weeks, in the process of seizing hundreds of billions of dollars from his political foes. Higher oil prices help his efforts to reshape the Saudi economy.
As liquidity dries up into the end of year and holidays, we may see oil find its way back up toward those November 2014 levels (low $70s)–where the whole price-bust debacle started.
Join our Billionaire’s Portfolio today to get your portfolio in line with the most influential investors in the world, and hear more of my actionable political, economic and market analysis. Click here to learn more.