July 30, 5:00 pm EST
The Nasdaq continued to slide today. Stock indices tend to go down a lot faster than they go up. The tech giant-driven Nasdaq was up over 15% year-to-date, just a few days ago, and has now given up more than 4% from the highs.
Not surprisingly, as people run for the exit doors on the big tech giants (taking profits), we’re seeing money rotate into the blue-chip value stocks.
The Dow and S&P 500 did much better than the Nasdaq today, which continues to slowly correct the big performance gap of the year (where the Nasdaq was up 15% at one point, while the DJIA was flat on the year).
Now, the biggest event of the week for markets may take place tonight. We hear from the Bank of Japan on monetary policy. We’ve discussed, many times, the role that Japan continues to play in our interest rate market.
Despite seven hikes by the Fed from the zero-interest-rate-era, our 10-year yield has barely budged. That’s, in large part, thanks to the Bank of Japan. Japan’s policy on pegging its 10-year yield at ZERO has been the anchor on global interest rates.
As I’ve said, when they finally signal a change to that policy, that’s when (our) rates will finally move. And that may be tonight. There is speculation that they may adjust UP that target on their 10-year yield. That would represent a dialing back of the BOJ’s QE program, which would signal the initial steps of exiting the crisis-era QE program.
What would that do? If the BOJ does indeed adjust their “yield curve control” policy, it should send global interest rates higher. That would put our ten-year yields back above 3%, which has been a level that has caused some uneasiness in markets. This time around, a move back above three percent would reflect a steepening U.S. yield curve which may be perceived as a positive, especially for those that have been concerned about the potential of seeing an inverted yield curve (i.e. a recession indicator).
If you haven’t joined the Billionaire’s Portfolio, where you can look over my shoulder and follow my hand selected 20-stock portfolio of the best billionaire owned and influenced stocks, you can join me here.
May 8, 2017, 4:00pm EST Invest Alongside Billionaires For $297/Qtr
 For the skeptics on the bull market in stocks and the broader economy, the reasons to worry continue to get scratched off of the list.
For the skeptics on the bull market in stocks and the broader economy, the reasons to worry continue to get scratched off of the list.
Brexit. Russia. Trump’s protectionist threats. Trump’s inability to get policies legislated. The French election.
The bears, those looking for a recession around the corner and big slide in stocks, are losing ammunition for the story.
With the threat of instability from the French election now passed, these are two of the more intriguing catch-up trades.
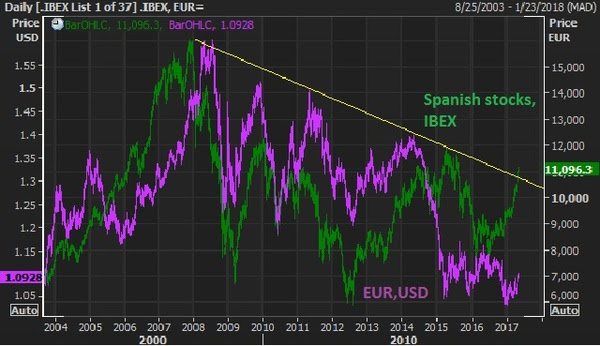
In the chart above, the green line is Spanish stocks (the IBEX). U.S., German and UK stocks have not only recovered the 2007 pre-crisis highs but blown past them — sitting on or near (in the case of UK stocks) record highs. Not only does the French vote punctuate the break of this nine year downtrend, but it has about 45% left in it to revisit the 2007 highs. And the euro, in purple, could have a dramatic recovery with the cloud of French elections lifted, which was an imminent threat to the future of the single currency.Next … Japanese stocks. While the attention over the past five months has been diverted toward U.S. politics and policies, the Bank of Japan has continued with unlimited QE. As U.S. rates crawl higher, it pulls Japanese government bond yields with it, moving the Japanese market interest rate above and away from the zero line. Remember, that’s where the BOJ has pegged the target for it’s 10 year yield – zero. That means they buy unlimited bonds to push the yield back down. That means they print more and more yen, which buys more and more Japanese stocks.
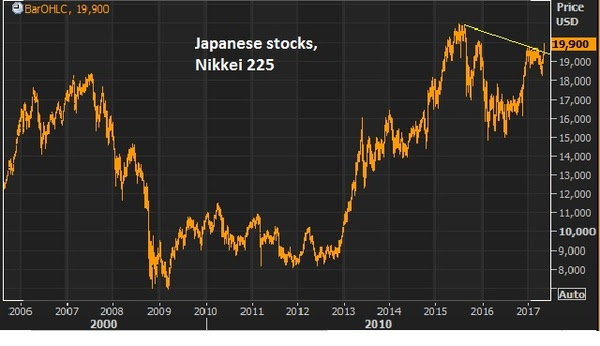
The Nikkei has been one of the biggest movers over the past couple of weeks (up almost 10%) since it was evident that the high probability outcome in the French election was a Macron win.Again, German, U.S., and UK stocks are at or near record highs. The Nikkei has been trailing behind and looks to make another run now, with 25,000 in sight.If you need more convincing that stocks can go much higher, Warren Buffett reiterated over the weekend that this low interest rate environment and outlook makes stocks “dirt cheap.” Last year he made the point that when interest rates were 15% [in the early 1980s], there was enormous pull on all assets, not just stocks. Investors have a lot of choices at 15% rates. It’s very different when rates are zero (or still near zero). He said, in a world where investors knew interest rates would be zero “forever,” stocks would sell at 100 or 200 times earnings because there would be nowhere else to earn a return.
Buffett essentially said at zero interest rates into perpetuity, the upside on the stock market (and any alternative asset class with return) is essentially infinite, as people are forced to find return by taking risk. Why you would buy a treasury bond that has no growth, and little-to-no yield and the same or worse balance sheet than high quality dividend stock.
This “forcing of the hand” (pushing investors into return producing assets) is an explicit objective by the interest rate policies of the Fed and the other major central banks of the world. They need us to buy stocks. They need us to spend money. They need economic growth.
If you have an brokerage account, and can read a weekly note from me, you can position yourself with the smartest investors in the world. Join us in The Billionaire’s Portfolio.
September 21, 2016, 4:40pm EST
Yesterday we talked about the two big central bank events in focus today. Given that the Bank of Japan had an unusual opportunity to decide on policy before the Fed (first at bat this week), I thought the BOJ could steal the show.
Indeed, the BOJ acted. The Fed stood pat. But thus far, the market response has been fairly muted – not exactly a show stealing response. But as we’ve discussed, two key hammers for the BOJ in achieving a turnaround in inflation and the Japanese economy are: 1) a weaker yen, and 2) higher Japanese stocks.
Their latest tweaks should help swing those hammers.
Bernanke wrote a blog post today with his analysis on the moves in Japan. Given he’s met with/advised the BOJ over the past few months, everyone should be perking up to hear his reaction.
Let’s talk about the moves from the BOJ …
One might think that the easy, winning headline for the BOJ (to influence stocks and the yen) would be an increase in the size of its QE program. They kicked off in 2013 announcing purchases of 60 for 70 trillion yen ($800 billion) a year. They upped the ante to 80 trillion yen in October of 2014. On that October announcement, Japanese stocks took off and the yen plunged – two highly desirable outcomes for the BOJ.
But all central bank credibility is in jeopardy at this stage in the global economic recovery. Going back to the well of bigger asset purchases could be dangerous if the market votes heavily against it by buying yen and selling Japanese stocks. After all, following three years of big asset purchases, the BOJ has failed to reach its inflation and economic objectives.
They didn’t take that road (the explicit bigger QE headline). Instead, the BOJ had two big tweaks to its program. First, they announced that they want to control the 10-year government bond yield. They want to peg it at zero.
What does this accomplish? Bernanke says this is effectively QE. Instead of telling us the size of purchase, they’re telling us the price on which they will either or buy or sell to maintain. If the market decides to dump JGB’s, the BOJ could end up buying more (maybe a lot more) than their current 80 trillion yen a year. Bernanke also calls the move to peg rates, a stealth monetary financing of government spending (which can be a stealth debt monetization).
Secondly, the BOJ said today that they want to overshoot their 2% inflation target, which Bernanke argues allows them to execute on their plans until inflation is sustainable.
It all looks like a massive devaluation of the yen scenario plays well with these policy moves in Japan, both as a response to these policies, and a complement to these policies (self-reinforcing). Though the initial response in the currency markets has been a stronger yen.
If you’re looking for great ideas that have been vetted and bought by the world’s most influential and richest investors, join us at Billionaire’s Portfolio. We have just exited an FDA approval stock for a quadruple. And we’ll be adding a two new high potential billionaire owned stocks to the portfolio very soon. Don’t miss it. Join us here.
September 19, 2016, 2:00pm EST
We have two big central bank meetings this week–BOJ and the Fed. With that, as we head into the week, let’s look at a key chart.

This chart is from a St. Louis Fed blog post last year. The inflation data, however, is all up-to-date. The Fed says “the chart above shows eight series that receive a lot of attention in the context of policy.”
So according to this chart, last year, as the Fed was building into its first rate hike to move away from emergency level rates and policies, the inflation data was looking soft. The Fed was telegraphing, clearly, a September hike, though six of the eight inflation measures in the chart above were running south of their target of 2% in the middle of last year. The headline inflation number for September, their preferred date of a hike, was zero!
Of course, after markets went haywire following China’s currency devaluation in August of last year, the Fed balked and stood pat. When things calmed, in December, they made their move. And at the same meeting, they projected to hike FOUR times this year. So far it hasn’t happened. It’s been a one and done.
Moreover, as of March of this year, they took two of those projected hikes off the table, and guided lower on growth, lower on inflation and a lower rate trajectory into the future. I would argue removing two hikes from guidance was effectively easing.
But if we look at the chart above, where inflation stands now relative to the middle of last year, when they were all “bulled-up” on rates, the story doesn’t jive. By all of the inflation measures, the economy is clearly running hotter (a relative term). Five of the eight inflation measures are running ABOVE the Fed’s 2% target (the horizontal black line in the chart). Yet, aside from a few Fed hawks that have been out trying to build expectations for a rate move soon, on balance, the messaging from the Fed has been mixed at best, if not dovish.
The Bernanke-led Fed relied heavily on communication (i.e. massaging sentiment and perception) to orchestrate the recovery, but the Fed, under Yellen, has been a communications disaster.
Join us here to get all of our in-depth analysis on the bigger picture, and our carefully curated stock portfolio of the best stocks that are owned and influenced by the world’s best investors.
2/2/16
It’s unimaginable that governments and central banks that have coordinated and committed trillions of dollars in guarantees, backstops, commitments and outright bailouts will stand by and let weak oil prices (rigged by OPEC) undo everything they’ve done over the past seven years to create stability and manufacture a global economic recovery.
Oil represents a systemic threat to the global economy. Just as housing created a cascade of trouble, through the global financial system, then through countries, the oil price crash can do the same.
When you see forecasts of $20 oil or lower, and some of it is coming from Wall Street, these people should also follow by telling you to buy guns and build a bunker, because that’s what you would need if oil went there and stayed there.
Not to mention, if they believe in that forecast, they should be formulating a plan for what they will do to make a living going forward, because their employers will likely go bust in that scenario.
The persistence of lower oil, especially less than or equal to $20 oil, would financially ruin the U.S. energy sector. Oil producing countries would be next, starting with Russia (and ultimately reaching the big OPEC nations). A default in Russia would create tremors in countries that hold Russia sovereign debt and rely on trade with Russia. Remember the fallout from the Asian Crisis? A default in Russia was the catalyst. Oil driven sovereign defaults would create a massive flight of global capital to safety and global credit/liquidity would dry up, again. All of this would put the world’s banks back on the brink of failure, just as we experienced in 2008. The only problem is, this time around, the global economy cannot absorb another 2008. Governments and central banks have fired their bullets and have nothing left to fend off another near global economic apocalypse.
With that, we have to believe that this crash in oil prices will not persist, especially when it’s being rigged by OPEC. Intervention now (or soon) is easy (relatively speaking) and returns the world to the recovery path. Intervention too late will require more resources than are available.
To follow the stock picks of the world’s best billionaire investors, subscribe at Forbes Billionaire’s Portfolio.
What’s the solution? An OPEC cut in production has a way of swinging oil in the other direction dramatically. Back in 1986, just a hint of an OPEC cut swung oil by 50% in just 24 hours. This assumes that the pressure builds on OPEC and they realize that the game of chicken that they are playing with U.S. producers has put themselves, also, precariously close to an endpoint.
Alternatively, we made the case last week that either China, the Bank of Japan or the European Central Bank could step in and outright buy commodities as a policy response to their ailing economies. Both the ECB and the BOJ in the past two weeks have said that there are “no limits” to what they can buy as part of their respective QE programs. That would immediately put a floor under crude, and likely global stocks, commodities and put in a top in sovereign bonds. Remember, when China stepped in, bought up and hoarded dirt cheap commodities in 2009, oil went from $32 to above $100 again.
So what’s the latest on oil?
Chart
This morning, the threat intensified. Oil dropped 5%, trading below the very key level of $30 per barrel. It was driven by an earnings report from the huge oil and gas company, BP. It reported a $6.5 billion loss. The company followed with an announcement of 7,000 job cuts by the end of 2017. Shares of BP stock are now trading back to 2010 levels, when the company was facing the prospects of bankruptcy after the fall–out from its gulf oil spill. This is one of the largest oil and gas companies in the world trading at levels last seen when people were speculating on its demise.
With the move in oil this morning, global stocks took another hit. Commodities were hit and sovereign debt yields were hit (with U.S. 10–year yields falling below 1.9%).
While there is a lot of talk about China and concerns there, clearly oil is what is dictating markets right now.
Take a look at this chart of oil vs. the S&P 500…

You can see the significant correlation historically in the price of oil and stocks. And you can see where oil and stocks came unhinged back in July 2014. The dramatic disconnect started in November 2014 (Thanksgiving Day) when an OPEC meeting concluded. The poorer members of OPEC called for production cuts. Saudi Arabia blocked the requests. That set off the plunge in oil prices.
You can see clearly in this chart where the price of oil is projecting the S&P. And stocks at those levels suggest the scenario we described above (global apocalypse round 2).
Again, a capitulation from OPEC is probably less likely. More likely, a central bank steps in to become an outright buyer of commodities (especially cheap oil). For those that have been shorting oil (and remain heavily short), either scenario would put them out of business quickly.
At this stage, OPEC is not just in a price war with U.S. shale producers, but it’s playing a game of chicken with the global economy. We’ve had plenty of events over the past seven years that have shaken confidence and have given markets a shakeup – European sovereign debt, Greece potentially leaving the euro, among them. In Europe, we clearly saw the solution. It was intervention. Oil prices are creating every bit as big a threat as Europe was; it’s reasonable to expect intervention will be the solution this time as well.
Bryan Rich is co-founder of Billionaire’s Portfolio, a subscription-based service that empowers average investors to invest alongside the world’s best billionaire investors. To follow the stock picks of the world’s best billionaire investors, subscribe at Billionaire’s Portfolio.
1/29/16
The Bank of Japan stepped in overnight and put a floor under stocks. Only 6 of 42 economists at Bloomberg thought they might do something.
We made the case over the past couple of days that they needed to. The opportunity was ripe, and we thought they would take advantage. They did.
Of course, that’s all the media is talking about today. The word “surprise” is in the headline of just about every major financial news publication on the planet with respect to this BOJ move (WSJ, Reuters, BBC, NYTimes … you name it).
Remember, we said earlier this week, the Fed was just a sideshow and the main event was in Japan. If you understand the big picture: 1) that central banks are still in control, 2) that the baton has been passed from the Fed to the BOJ and the ECB, and 3) that they (central banks) need stocks higher, then this move comes as no surprise.
To follow the stock picks of the world’s best billionaire investors, subscribe at Forbes Billionaire’s Portfolio.
Today we want talk a bit about what these central banks have done, what they are doing and why it works. We often hear the media, analysts, politicians, Fed-haters saying that QE hasn’t worked.
Okay, so QE hasn’t directly produced inflation and solved the world’s problems as the Fed might have expected when they launched it in late 2008. But it has produced a very important direct benefit and indirect benefit. The direct benefit: The Fed has been successful at driving mortgage rates lower, which has ultimately translated to rising house prices (along with a slew of other government subsidized programs). That has been good for the economy.
The indirect benefit: As Bernanke (the former Fed Chair) said explicitly, “QE tends to make stocks go up.” Stocks have gone up – a lot. That has been good for the economy.
But we need a lot more – they need a lot more. Here’s a little background on why…
The Fed has told us all along they want employment dramatically better, and inflation higher. They’ve gotten better employment. They haven’t gotten much inflation. Why? In normal economic downturns, making money easier to borrow tends to increase spending, which tends to increase demand and inflation. In a world that was nearly destroyed by overindebtedness, people (businesses, governments) are focused on reducing debt, not taking on more debt (regardless of how “easy” and cheap you make the money to access).
With that, their best hope to achieve those two targets (employment and inflation) has been through higher stocks and higher housing prices. Strength in these key assets has a way of improving confidence and improving paper wealth. Increasing wealth makes people more comfortable to spend. Better spending leads to hiring. A better job market can lead to inflationary pressures. That’s been the game plan for the Fed. And that’s the gameplan for Europe and Japan.
To follow the stock picks of the world’s best billionaire investors, subscribe at Forbes Billionaire’s Portfolio.
So how do they promote higher stock prices? They do it by promising investors that they will not let another shock event destabilize the world and global financial markets. They’ve promised that they will “stand ready to act” (the exact words uttered by the Fed, the ECB and the BOJ). So, they spent the better part of the past eight years promising to do “whatever it takes” (again exact words of the ECB and BOJ).
The biggest fear investors have is another “Lehman-like event” that can crash stocks, the job market and the economy. The thought of it makes people want to hold on tight to their money. But when the central banks promise to do anything and everything to prevent another shock, it creates stability and confidence to invest, to hire, to take some risk again. That’s good for stock prices.
Now, despite what we’ve just said, and despite the aggressive actions central banks have taken in past years (including the BOJ’s actions last night to push interest rates below zero) and their success in manufacturing confidence and recovery, when stocks fall, people are still quick to talk about recession and gloom and doom. On every dip in stocks since the culmination of the global financial crisis in 2007-2008, the comparisons have been made to that period.
First, they’re ignoring what the central banks have been telling us. “We’re here, ready to act.” Second, and again, things are very, very different than they were in 2007-2008. In that period, global credit was completely frozen. Banks were failing, and the entire financial system was on the precipice of failing. And at that point, it was unclear what could be done and what actions would be taken to try to avert disaster. That uncertainty, the thought of losing 100 years of economic and social progress across the globe, can easily send people scurrying for cash, pulling money from everywhere and protecting what they have. And that uncertainty can, understandably, result in stock prices getting cut in half – a stock market crash.
Now, what’s happening today? The financial system is healthy. Credit is flowing. Unemployment is very close to long-term historical norms. The U.S. economy is growing. The global economy is growing. The best predictor of recession historically is the yield curve. It shows virtually no chance of recession on the horizon. So the economic environment is very different. Still, the biggest difference between that period and today is this: We didn’t have any idea what could be done to avert the disaster OR how far central governments and central banks would go (and could go) to fight it. Now we know. It’s all-in, all or nothing. There is no ambiguity. With that, the central banks will not fail and cannot fail. And remember, they are working in coordination. No one wins if the world falls apart.
With all of this in mind, any decline in stocks, driven by fear and misinformation, offers a great buying opportunity, not an opportunity to run.
We’ll talk Monday about the very strong, and rational fundamental case for stocks to go much higher. On that note, today we’re wrapping up one of the worst January’s on record for stocks, which has given us a great opportunity to buy at a nice discount.
Bryan Rich is co-founder of Billionaire’s Portfolio, a subscription-based service that empowers average investors to invest alongside the world’s best billionaire investors. To follow the stock picks of the world’s best billionaire investors, subscribe at Billionaire’s Portfolio.





